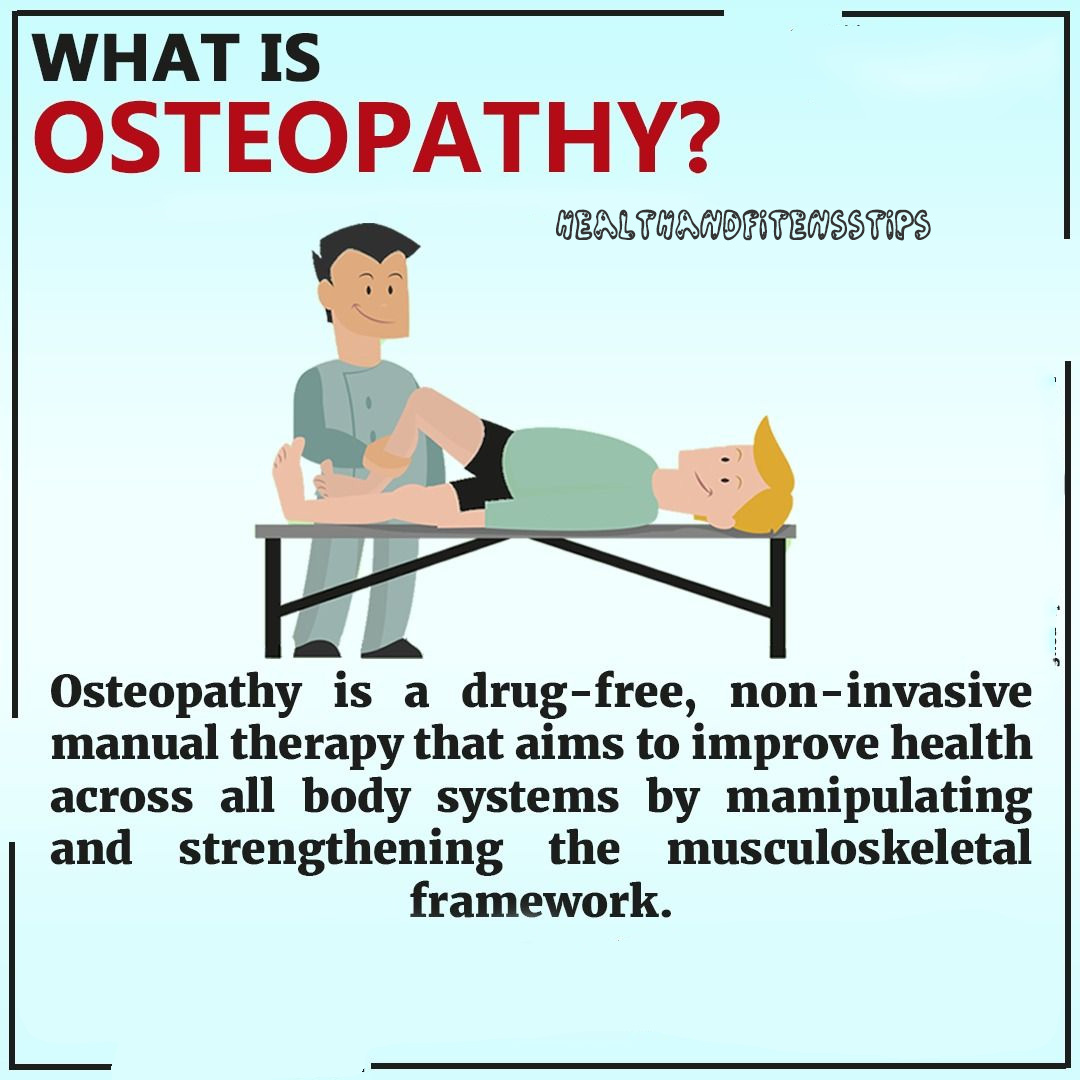
Osteopathy is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes the physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones (see medical studies about Osteopathy), through the therapeutic application of manually guided forces by a practitioner, intended to improve physiologic function and/or support homeostasis that has been altered by somatic dysfunction. The standard methods include:
Active Method: A technique in which the person voluntarily performs an osteopathic practitioner-directed motion.
Passive Method: Based on techniques in which the patient refrains from voluntary muscle contraction.
Direct Method (D/DIR): An osteopathic treatment strategy by which the restrictive barrier is engaged and a final activating force is applied to correct somatic dysfunction.
Indirect Method (I/IND): A manipulative technique where the restrictive barrier is disengaged and the dysfunctional body part is moved away from the restrictive barrier until tissue tension is equal in one or all planes and directions
In some countries osteopathy is practiced by specially-trained doctors and physiologists, but osteopaths trained outside of the U.S. are generally not physicians and use only non-invasive manual therapies, though they may provide nutritional, postural, and other health advice. To avoid confusion the American Osteopathic Association and the American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine recommend using the terms osteopathic physician (for U.S.-trained only) and osteopathic medicine in reference to osteopathic medicine as practiced in the United States.